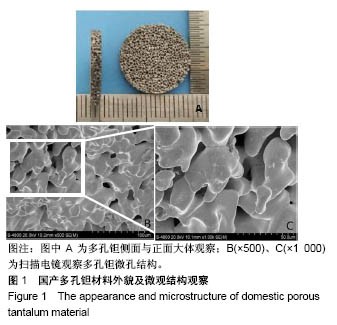
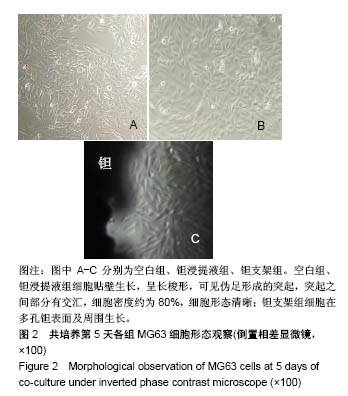
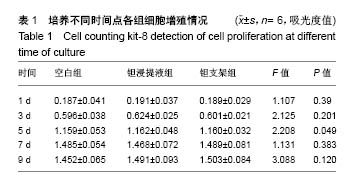
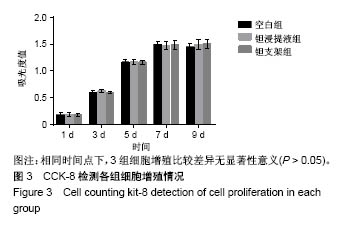
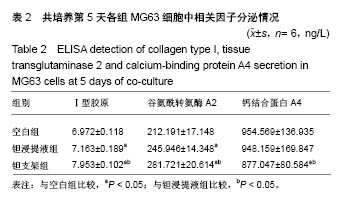
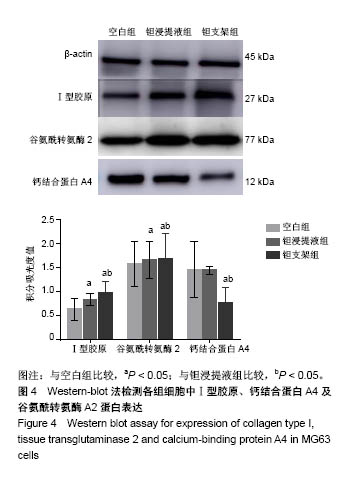
| [1] Xing J, Jin H, Hou T, et al. Establishment of a bilateral femoral large segmental bone defect mouse model potentially applicable to basic research in bone tissue engineering. J Surg Res.2014;192(2):454-463.[2] Drosse I, Volkmer E, Capanna R, et al. Tissue engineering for bone defect healing: an update on a multi-component approach. Injury. 2008;39(2):S9-S20.[3] Laurencin C, Khan Y, Elamin SF. Bone graft substitutes. Skeletal Radiol. 2007;36(12):1105-1107.[4] 邓子文, 黄东.同种异体骨移植修复骨缺损的应用进展[J].山东医药,2017,57(32):98-100.[5] Kato H, Nakamura T, Nishiguchi S, et al. Bonding of alkali- and heat-treated tantalum implants to bone. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;53(1):28-35.[6] Bermúdez MD, Carrión FJ, Martínez-Nicolás G, et al. Erosion–corrosion of stainless steels, titanium, tantalum and zirconium. Wear. 2005; 258(1):693-700.[7] Balla VK, Bodhak S, Bose S, et al. Porous tantalum structures for bone implants: fabrication, mechanical and in vitro biological properties. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(8): 3349-3359.[8] Hacking SA, Bobyn JD, Toh K, et al. Fibrous tissue ingrowth and attachment to porous tantalum. J Biomed Mater Res. 2015;52(4):631-638.[9] Matsuno H, Yokoyama A, Watari F, et al. Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of refractory metal implants, titanium, hafnium, niobium, tantalum and rhenium. Biomaterials. 2001;22(11): 1253-1262.[10] Li X, Wang L, Yu X, et al. Tantalum coating on porous Ti6Al4V scaffold using chemical vapor deposition and preliminary biological evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013; 33(5):2987-2994.[11] Wauthle R, Vand SJ, Amin YS, et al. Additively manufactured porous tantalum implants. Acta Biomaterialia. 2015;14: 217-225.[12] 王茜.国产多孔钽对成骨生物学效应影响机制的体外研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015.[13] 赖振权,崔逸爽,陈超,等.新型骨植入材料多孔钽-骨结合界面成骨以及相关成骨因子的表达及意义[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(18):2789-2795.[14] 沈小辉,杨华清,唐文娟,等. 1α,25-二羟维生素D_3对成骨细胞增殖分化、I型胶原及核心结合因子α-1基因表达的影响[J].实用老年医学,2014,28(6):500-505.[15] 刘刚, 胡蕴玉, 廉凯,等.Ⅰ型胶原对骨髓基质干细胞粘附及分化的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2002,17(5):361-363.[16] Lee HJ, Chang HL. Transglutaminase-2 Is Involved in Expression of Osteoprotegerin in MG-63 Osteosarcoma Cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013;21(3):204-209.[17] Zhou M, Li ZQ, Wang ZL. S100A4 upregulation suppresses tissue ossification and enhances matrix degradation in experimental periodontitis models.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015; 36(11):1388-1394.[18] Mankani MH, Afghani S, Franco J, et al. Lamellar spacing in cuboid hydroxyapatite scaffolds regulates bone formation by human bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011; 17(11-12):1615-1623.[19] Cai F, Wu XT, Xie XH, et al. Evaluation of intervertebral disc regeneration with implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) using quantitative T2 mapping: a study in rabbits. Int Orthop. 2015;39(1):149-159.[20] 王茜,张辉,耿丽鑫,等.MG63细胞与国产多孔钽材料共培养后成骨相关因子的表达研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(11): 1422-1427.[21] Zardiackas LD, Parsell DE, Dillon LD, et al. Structure, metallurgy, and mechanical properties of a porous tantalum foam. J Biomed Mater Res. 2015;58(2):180-187.[22] Shimko DA, Shimko VF, Sander EA, et al. Effect of porosity on the fluid flow characteristics and mechanical properties of tantalum scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2005;73(2):315-324.[23] Lachiewicz PF, Bolognesi MP, Henderson RA, et al. Can tantalum cones provide fixation in complex revision knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(1):199-204.[24] Hanzlik JA, Day JS.Bone ingrowth in well-fixed retrieved porous tantalum implants.J Arthroplasty.2013;28(6):922-927.[25] Howard JL, Kudera J, Lewallen DG, et al. Early results of the use of tantalum femoral cones for revision total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93(5):478-484.[26] 刘洪臣,路荣建. 新型多孔钽人工种植牙[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2016, 14(1):41-44.[27] Nakashima Y, Mashima N, Imai H, et al. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of total hip arthroplasties using porous tantalum modular acetabular components: 5-year follow-up of clinical trial. Mod Rheumatol. 2013;23(1):112-118.[28] 钟建鑫,节云峰, 罗金英,等.多孔钽颗粒在下颌骨缺损修复中的作用[J].第三军医大学学报, 2015, 37(12):1277-1280.[29] Aeschlimann D, Thomazy V.Protein crosslinking in assembly and remodelling of extracellular matrices: the role of transglutaminases.Connect Tissue Res. 2000;41(1):1-27.[30] Gelse K, Pöschl E, Aigner T.Collagens—structure, function, and biosynthesis.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55(12): 1531-1546.[31] 卫爱林,叶小丰,刘世清,等.磷酸三钙/透明质酸/Ⅰ型胶原/骨髓基质胞复合物修复骨缺损与自体骨的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(9):1779-1782.[32] Fortunati D, Chau DY, Wang Z, et al. Cross-linking of collagen I by tissue transglutaminase provides a promising biomaterial for promoting bone healing. Amino Acids. 2014;46(7): 1751-1761.[33] Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, et al. Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol. 1995;130(2):393-405.[34] Wang Z, Griffin M. The role of TG2 in regulating S100A4-mediated mammary tumour cell migration.Plos One. 2013;8(3):e57017. |
.jpg)
.jpg)